Treatment of lung cancer in clinics of Germany
Cancer of the respiratory system is the most common cause of death among all pathological neoplasms. This is a tumor that develops from cells of the lung tissue or bronchi. Fortunately, thanks to progress in diagnosing this disease, today the length and quality of life of those affected has improved significantly.
European medicine with experienced world-class oncologists plays a leading role in the fight against this disease. Often, patients in the final stages seek treatment for lung cancer in Germany, which requires the latest equipment and the use of advanced therapy methods - all this is provided at the highest level by German medical institutions.

Want to know how much the treatment costs?
Answer a few questions and get preliminary information about the cost of diagnosis and treatment!
Advantages of lung cancer treatment in Germany
Lung treatment in Germany is the optimal choice in terms of cost and quality of services offered. This is due to a number of unique advantages of German medicine in this area:
- Advanced diagnostic equipment. Thanks to generous government funding, German medical centers regularly update medical diagnostic equipment. The most modern CT, MRI, PET-CT scanners, X-ray machines, endoscopes and ultrasound stations are installed here. This makes it possible to diagnose a tumor of any location and stage.
- Access to the latest developments. Every year, more than 500 clinical trials of new methods for detecting and curing cancer are launched in Germany. Those who apply to have access to innovative developments, which significantly increases the chances of recovery.
- High quality standards. Oncology departments undergo regular certification to meet the highest international standards, and doctors constantly improve their skills and exchange experience with colleagues.
- Minimally invasive operations. Most interventions are performed using thoracoscopy. This helps preserve the ribs and speed up rehabilitation. In addition, German surgeons actively use robotics (Da Vinci) to remove tumors in inaccessible areas as carefully as possible.
- High-precision radiation therapy. The most modern accelerators are used: CyberKnife, Novalis Tx or TrueBeam STx. Stereotactic radiosurgery is actively used, during which the tumor is irradiated with millimeter precision, with virtually no damage to healthy organs. This significantly increases the chance of a positive result with minimal side effects.
- Quality medications. Only original antitumor and targeted medicines from pharmaceutical companies of the European Union are prescribed. This increases the chances of no relapse and does not pose a health hazard.
- Highly qualified doctors. German oncological surgeons, radiologists and thoracic surgeons undergo many years of specialized training in the best specialized medical centers not only in the country, but throughout the world. Many of them have scientific degrees and titles.
- Integrated approach. An individual plan is developed for each applicant, including the optimal combination of surgery, radiotherapy, drug therapy and rehabilitation. The oncology departments here are famous for their decent level of service and comfortable living conditions.
- For radiotherapy in Germany, the latest generation devices are used. Their accuracy is about 0.5 millimeters, which makes it possible to remove the tumor without harming and preserving healthy tissue. For comparison, clinics in Ukraine and post-Soviet countries use older linear accelerators, the accuracy of which is several centimeters. When operating on lung cancer in Germany, laparoscopic techniques are used, which allows the patient’s ribs to be preserved - the operation is performed through three small incisions up to 1 centimeter between the patient’s ribs.
- Prices for medical services in the country are regulated at the state level, so they vary greatly depending on the clinic. When choosing a medical institution, pay attention to the cost of related non-medical procedures - their prices can vary greatly. In addition, an operation with a regular doctor will be cheaper than with a professor or department head. Prices also depend on the stage of the disease (if in the initial stages of lung cancer only surgery or radiation therapy is sufficient, then in later stages chemotherapy or immunotherapy may be needed).
- Survival from this dangerous disease depends on its stage. If the tumor has not spread beyond the lung, then the chances are quite high and are about 60%. Things are worse if metastases have formed in the lymph nodes or distant organs. However, any conclusions can be drawn only after consultation with your doctor.
- Surgery is almost always necessary, but in Germany they use minimally invasive treatment methods, whereby not the entire lung is removed, but only the malignant tumor itself and a small area of tissue around it.
Diagnostics of lung cancer in German clinics
After hospitalization, the attending physician conducts a detailed survey about the nature of the complaints and medical history. This is followed by a complete clinical examination of all body systems. If necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed. If there is a suspicion of a tumor, the specialist develops an in-depth diagnostic plan, including laboratory and instrumental techniques.
Radiography
X-rays are prescribed for primary diagnosis in the treatment of lung cancer in Germany. The image obtained using ionizing radiation demonstrates the condition of the soft tissues, bronchi, and other anatomical structures of the chest.
Thanks to modern digital detectors, the sensitivity of radiography is very high - nodules measuring just a few millimeters are clearly visible in the images. The detected changes have a characteristic round shape and increased density.
CT chest
Computed tomography is also based on the use of X-rays, but provides more detailed information about the condition of the lungs. A series of images is taken in different planes, and then a computer processes the data obtained and creates a three-dimensional image of the area under study. In this way, it is possible to accurately determine the location, parameters and characteristics of the identified pathology.
Bronchoscopy
This diagnostic method is an important component of the examination if cancer is suspected. During the procedure, the doctor directly examines the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and takes samples for analysis.
The study involves a flexible bronchoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and a light source. The instrument is inserted through the nasopharynx or throat under general anesthesia. The optical system transmits the image to a computer, where the doctor can detect and evaluate changes.
Biopsy
To obtain material for laboratory study, a biopsy is performed under the control of ultrasound or computed tomography equipment. This helps to accurately visualize the tumor and safely enter it with a thin needle through a small hole in the intercostal space.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia, so it does not cause discomfort. The doctor receives several fragments of the affected area, which are fixed and sent for laboratory analysis. Results are usually ready within 5–7 days.
Laboratory research
The samples obtained in the laboratory are stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells. Then the histological type and grade of malignancy are determined.
Immunohistochemical analysis is also performed using specific antibodies to tumor proteins and receptors. In this way, mutations can be identified and the latest targeted drugs or immunotherapy can be selected.
PET-CT
Widely used to diagnose cancer and assess the extent of the process. Before the study, a radiopharmaceutical containing a positron isotope, which is actively absorbed by cancer cells, is injected intravenously. Then, in a special tomograph, a scan of the entire body is performed, during which radiation from the tissues from the disintegrated drug is recorded.
At the same time, a CT scan is performed to obtain anatomical images. The combination of PET and CT data provides comprehensive information about the location and size of the malignant formation, as well as the presence or absence of metastases.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI of the brain with contrast is prescribed for suspected metastatic brain lesions in lung cancer to exclude or confirm the diagnosis. The study is carried out using a tomograph using magnetic fields and radio waves.
This provides accurate images of the brain with millimeter resolution, which helps to identify even small lesions for subsequent actions - surgical removal or radiation.
Liquid biopsy
This is a high-tech blood test aimed at detecting circulating tumor cells that have migrated from the primary tumor or metastatic sites. Their presence clarifies the diagnosis and overall prognosis.
Liquid biopsy is fully approved by US and EU regulatory authorities, and has also been validated in clinical studies, allowing you to select the most effective personalized therapy in each specific case.
Endobronchial ultrasound
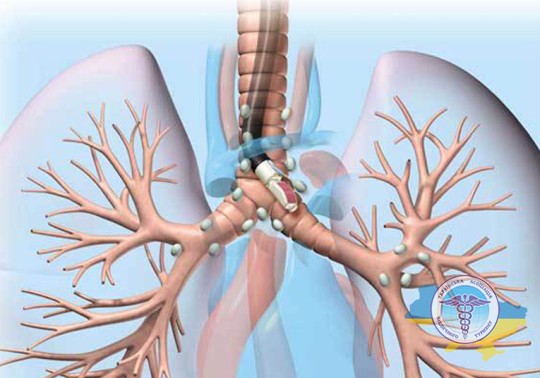
This type of ultrasound differs from conventional bronchoscopy by the presence of an ultrasound sensor at the end of the probe, which displays not only the inner surface of the bronchi, but also the surrounding organs, in particular the mediastinal lymph nodes.
The doctor can assess their size, structure and the presence of changes that may indicate metastatic lesions. There is also the possibility of targeted puncture of a lymph node under ultrasound guidance to collect material for biopsy and subsequent laboratory testing.
Thoracoscopy (VATS)
It is a minimally invasive endoscopic examination of the pleural cavity. The doctor gets the opportunity to directly examine the inner surface of the lung, the diaphragm and the mediastinum. Biopsies may be taken and small areas of inflammation or cysts may be removed. Thoracoscopy is performed under general anesthesia through small punctures in the chest wall.
Thoracentesis
This is a puncture of the pleural cavity using a needle to withdraw fluid for laboratory analysis, which is performed under local anesthesia. Analysis of pleural exudate can determine the presence of tumor markers and harmful foci to verify the diagnosis, assess the effectiveness of therapy and detect relapse.
Mediastinoscopy
An endoscopic method for diagnosing the mediastinum, which is performed under general anesthesia through a small incision in the neck. The doctor inserts a special probe with optics and lighting and examines the mediastinal lymph nodes.
If necessary, biopsies are taken for histological examination. Mediastinoscopy is low-traumatic and provides doctors with important diagnostic information about the extent of the process.
Videothoracoscopy
This type of diagnosis makes it possible to examine the pleural cavity, lung, mediastinum and diaphragm with a special video endoscope inserted through a puncture in the chest wall. Suspicious areas are taken for biopsy, and small lesions can be removed immediately during the procedure, which reduces trauma and rehabilitation time.
Wedge resection
It involves removing a small fragment of the lung along with the formation for subsequent histology. It is the area with the suspicious node that is resected, and the surrounding healthy tissue is preserved as much as possible. This makes it possible to obtain an accurate diagnosis, avoiding extensive lobectomy at the first stage. If the diagnosis is confirmed, an extended intervention is performed.
Lung cancer treatment methods in German clinics
The choice of the optimal treatment plan for lung cancer in German clinics is based on the results of a comprehensive examination of a particular patient. Factors such as the histological type, molecular genetic profile of the neoplasm, its localization and the extent of the process are taken into account.
The prescribed therapeutic course strictly complies with the current recommendations of leading specialized societies - the Association of German Oncology Clinics and the European Society of Medical Oncology. In this way, you can select a personalized and most effective action plan for everyone.
Surgery
German surgeons strive to preserve healthy lung tissue as much as possible - when the stage of the disease allows, they perform organ-preserving operations. The extent of resection depends on the size and location of the affected lesions. Below are the main types of surgical interventions used:
- Marginal (limited) resection. It involves excision of a formation with a thin layer (up to 1 cm) of surrounding unchanged lung tissue. It is used to remove small peripheral lesions in the absence of involvement of lymph nodes and adjacent structures (bronchi and vessels). In this way, it is possible to preserve the volume of functioning tissue as much as possible.
- Segmentectomy. Removal of the affected segment completely if the tumor is localized within one segment. Performed through open or thoracoscopic access. The segment, as an anatomical unit, is separated from its neighbors by its own pleura, vessels and bronchus, which makes it possible to perform anatomically accurate resection.
- Lobectomy. It involves removing the entire lobe of the lung (right or left) along with the affected area and lymph nodes. The operation used is considered the “gold standard” in the field of oncology.
- Pneumonectomy. Involves radical removal of the entire lung. Indicated for central or extensive organ damage, involvement of the root of the lung and further tumor growth. It is the most extensive and traumatic intervention.
- Video thoracoscopic operations. The technique consists of performing the intervention through small punctures of the intercostal spaces using video endoscopic technology. Allows you to significantly reduce trauma and speed up recovery after surgery.
Conservative methods
In addition to surgery and radiotherapy, there are also conservative (non-surgical) approaches that can be used either individually or in combination with other methods of treatment.
Chemotherapy
It implies the use of special antitumor drugs - cytostatics, which tend to suppress cell growth and division. According to current international protocols, chemotherapy is usually prescribed after surgery to destroy remaining lesions and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Chemical drugs are administered cyclically with breaks to restore the body, most often the method of intravenous infusion through a dropper is used.
Radiation therapy
Its essence is the use of high-energy ionizing radiation, which destroys the structure of neoplasms. Irradiation is performed either externally or internally, introducing a radiation source directly into the tumor or next to it.
The latest equipment in the field of radiotherapy (cyberknife, gamma knife, etc.) affects the tumor with high precision and preserves the healthy areas adjacent to it as much as possible. Radiotherapy is prescribed in courses - from 4 to 5 doses per week. The irradiation procedure itself is painless, but subsequent side effects may occur in the form of skin irritation or gastrointestinal complications.
Targeted therapy
One of the most modern high-tech areas in the treatment of respiratory tract oncology. Its essence is to influence specific molecular targets that play a key role in tumor growth. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, targeted medications specifically block only altered signaling pathways in pathological foci, minimally affecting the healthy area.
Target has higher selectivity and is less likely to cause side effects compared to cytostatics. Medications are most often taken in tablet form. According to international recommendations, in Germany this method is used for metastases, less often in neoadjuvant or adjuvant regimens.
Immunotherapy
Its essence lies not in a direct effect on the affected areas, but in mobilizing and strengthening the human immune system’s own antitumor mechanisms. Often, the immune system is able to independently recognize and eliminate potentially dangerous foreign agents.
However, cancer cells have developed clever mechanisms that allow them to hide from immune surveillance and suppress the antitumor response. Immunotherapeutic agents block the camouflage mechanisms of the tumor, depriving it of “invisibility” to the immune system.
For immunotherapy, checkpoint inhibitors (nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, etc.), as well as cytokines and specific vaccines are prescribed. If chemotherapy is ineffective, immunotherapy according to international recommendations is prescribed to patients with metastatic non-small cell cancer.
Symptomatic and supportive therapy
Along with radical methods that are aimed at destroying cancer, symptomatic and supportive treatment plays an important role in the comprehensive fight against cancer. Its goal is to make you feel better, relieve pain and correct complications.
The main components of symptomatic support include: prescription of painkillers, prevention of infections, correction of breathing disorders, psychotherapy, nutritional support and a number of other measures aimed at stabilizing the condition, improving the quality of life and preventing the development of complications.
Innovative techniques
Despite progress in early diagnosis and the development of traditional medicine, the effectiveness of treatment for lung metastases in Germany remains low. In this regard, close attention is paid to the development and implementation of innovative high-tech approaches based on the latest advances in the field of molecular biology, genetics, immunology and other related disciplines.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
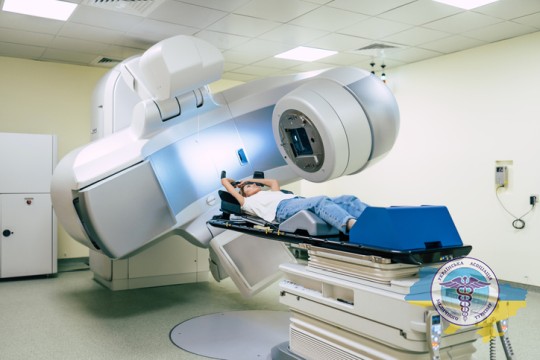
One of the promising minimally invasive approaches to radiotherapy is radiosurgery using ionizing radiation accelerators. Thanks to precision three-dimensional planning and dose delivery systems, radiation surgery delivers a targeted blow to the tumor without resorting to surgery. An important advantage is the ability to preserve adjacent healthy tissue.
Endoluminal brachytherapy
During brachytherapy, sources of ionizing radiation are introduced directly into the tumor or placed in proximity to it. Unlike traditional external beam radiotherapy, when radiation is delivered through the skin, brachytherapy involves interstitial radiation.
In this way, it is possible to concentrate the maximum dose in the source area, act locally and minimize irradiation of healthy areas of the organ.
Checkpoint inhibitors
One of the equally promising areas of immunotherapy is the use of targeted antibodies - immune checkpoint inhibitors. They block the interaction between cancer cells and T lymphocytes by disrupting the function of immune receptors and their ligands.
Normally, these receptor pairs perform a regulatory role, limiting excessive activation of the immune system and the development of responses. However, cancer cells use certain points to suppress the antitumor immune response and evade the body's response. Checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab and atezolizumab) block these pathways and help the immune system recognize and destroy pathologies.
Palliative care
Unfortunately, in some cases, especially in later stages, the tumor cannot be completely cured due to its large size, the presence of distant metastases, or low sensitivity to therapy.
In such situations, palliative therapy comes to the fore, the main objectives of which are to prevent further progression of the disease, prolong life as much as possible and relieve associated symptoms.
Proton therapy
It is an innovative type of irradiation with a flow of protons - positively charged elementary particles. Unlike traditional X-rays, the penetration depth of protons can be precisely controlled, after which the particles deposit almost all of their energy directly at the lesion.
This key advantage allows for minimal radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissue compared to other types of radiation. Reducing radiation exposure to the heart, spinal cord, esophagus and other parts of the respiratory organs significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Embolization
The essence of endovascular vascular occlusion is the minimally invasive closure of the lumens that supply the affected area of the vessels with the help of special emboli. In advanced stages of cancer, the most common target for embolization is the bronchial arteries that supply the tumor. Blockage of the lumen of these arteries leads to ischemia and necrosis of the formation, which slows down the progression of the disease and improves the prognosis in advanced stages.
Radiofrequency ablation
The essence of ablation is the thermal destruction of cancer cells by heating from the inside to high temperatures with special applicators. In this case, high-frequency electromagnetic waves are used to heat tumor foci and cause their coagulation necrosis.
Cost of treatment for lung cancer in Germany
The cost of treatment for cancer in Germany is generally comparable to that of other developed countries. German oncologists and radiologists actively combine traditional approaches with the latest advances in personalized medicine and immunotherapy. This allows high cure rates to be achieved at a relatively reasonable cost.
In general, the following factors influence the overall price tag:
- Stage. At the initial stages, when the formation is localized and has not metastasized, radical treatment using surgical excision is possible. At advanced stages, long courses of expensive drug therapy are required, which significantly increases the total cost.
- Cost of medicines. Modern chemotherapy drugs, targeted drugs and immune inhibitors from different manufacturers differ significantly in price, sometimes several times. In addition, dosage regimens vary in duration - from several months to 5 years.
- Qualification of an oncologist. Involving professors, heads of departments and leading European specialists in a certain type of pathology in the process is more expensive than ordinary doctors. However, this guarantees the most modern approaches and the highest efficiency.
- Type of medical facility. In Germany there are private institutions, public medical centers and university clinics at medical faculties. In private hospitals, the comfort of stay and service are usually higher and, accordingly, more expensive.
- Additional services. For a single superior room, meals on an individual menu, an interpreter, transfers, concierge service and other services you will have to pay extra separately.
The following are the estimated prices for lung cancer treatment in Germany:
| Procedure | Cost, euro |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive diagnostics | 5500 |
| Doctor consultation | 100 |
| Ultrasound | 100 |
| MRI | 500 |
| PET-CT | 2000 |
| Histology | 800 |
| Genetic testing | 1500 |
| Radiation therapy | 2000 |
| Immunotherapy | 5000 |
| Plastic surgery | 3000 |
| Rehabilitation | 2000 |
| Day hospital | 300 |
| Chemotherapy (1 course) | 5500 |
| Robotic surgery (Da Vinci) | 17000 |
| Proton therapy | 50000 |



