Treatment of a hernia of backbone in Germany
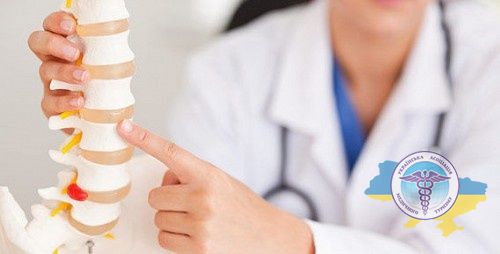
Intervertebral herniation is a common disease of the spine in which the intervertebral disc (IVD) is displaced, and the fibrous ring is ruptured. Although it is rarely life-threatening in itself, ignoring the symptoms can lead to serious complications such as paralysis or sensory disturbances.
Treatment of spinal hernia in Germany is famous for its high quality and compliance with international standards. Every year, thousands of patients from all over the world come to German clinics for complex therapy. High treatment results (up to 97% of positive outcomes) explain the popularity of German medicine.

Want to know how much the treatment costs?
Answer a few questions and get preliminary information about the cost of diagnosis and treatment!
Advantages of spinal hernia treatment in Germany

The quality of medicine in German clinics is due to the high level of government funding, which makes it possible to regularly modernize equipment, conduct scientific research and improve the quality of service.
The main advantages of treating intervertebral hernia in Germany:
- State control. According to the general strategy of the German Ministry of Health, clinics must have a high level of qualified doctors, technical equipment and services in order to be able to receive foreign patients.
- Innovative research. Leading German research institutes and medical centers are actively developing and implementing effective methods of diagnosis and therapy in the field of neurology and neurosurgery.
- Highly qualified doctors. For more than 10 years, German neurosurgeons have been actively and successfully performing thousands of high-tech, minimally invasive operations to remove spinal hernias. This is a unique practical experience that is not yet available to medical specialists in the CIS countries.
- Modern medical equipment. High technologies optimize the course of operations and minimize the risks of complications. High-precision navigation systems, surgical lasers, robotic assistants and other innovative solutions are widely used in operating rooms.
- Speed and accuracy of diagnosis. This is achieved through comprehensive diagnostics using the most modern high-tech equipment of the latest generation with high-resolution images. A complete examination helps to identify all abnormalities and changes in the body in just 48 hours.
- Cure in the later stages of the disease. An individual treatment program is developed for each patient, taking into account the medical history and characteristics of the current condition.
- Minimally invasive and non-invasive techniques. Priority is given to gentle therapy, which ensures recovery with minimal intervention. Pinpoint radiation therapy, radiofrequency ablation and other advanced technologies are actively used.
Diagnostics of intervertebral hernia in German clinics
Examinations to detect the disease are carried out in accordance with international standards and using the latest technologies.
Radiography
Gives a general idea of the condition of the spine and may indirectly indicate the presence of pathologies, but does not provide their complete visualization. The procedure takes about 5 minutes.
During the examination, the patient stands in front of the detector and holds his breath for several seconds while the scan takes place. X-rays are also often used to rule out other spinal disorders during the diagnosis process.
Computed tomography
Provides accurate 3D images of the spine and surrounding tissues, allowing you to clearly visualize changes in the fibrous rings, their size and direction of protrusion.
The study takes from 15 to 60 minutes, during which the patient lies motionless on a special platform inside the device. The scanner makes several projections, which are further processed by a computer.
Myelography
This is an invasive diagnostic procedure that involves injecting a contrast X-ray directly into the spinal canal.
Due to the distribution of contrast in this area, it is possible to obtain a very clear image of the nerve structures and assess the degree of displacement and deformation of the spinal cord.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is considered the most informative method for diagnosing spinal hernia in German clinics. It provides a detailed three-dimensional image of the condition of the spinal column, the degree of compression of nerves and bone tissue.
MRI accurately determines the localization of pathologies, their size and shape, the direction of exit beyond the fibrous ring, as well as the degree of deformation of the dural sac and spinal cord.
Electromyography
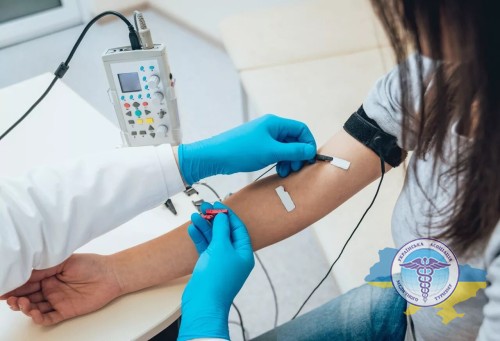
The method is used to diagnose disorders of the functioning of peripheral nerves. It helps assess the degree of damage to nerve fibers, which is important for predicting the restoration of sensitivity.
There are two main types of research:
- In invasive needle electromyography, a special electrode with a thin needle is inserted directly into the muscle being studied.
- Non-invasive surface electromyography uses skin sensors.
In both cases, nerve stimulation records electrical activity in the muscle, which can indicate the presence of damage.
Methods of treating intervertebral disc herniation in German clinics
Therapy of spine diseases in German clinics is carried out comprehensively using both conservative and surgical methods in accordance with international standards.
Non-surgical treatment of the spine
At the first stage, patients are recommended non-invasive therapy, which will be aimed at reducing pain and restoring spinal function. This will avoid surgery in approximately 80% of cases.
Drug therapy
It is the basis for non-surgical treatment of the spine in Germany in the initial stages of the disease. Helps eliminate pain and inflammation, restores joint mobility and promotes tissue regeneration without surgical intervention.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs effectively relieve pain and swelling, and muscle relaxants eliminate back spasms. Corticosteroids, diuretics, antioxidants and B vitamins are also used to improve the functioning of the nervous system. A course of drugs is usually prescribed for a period of at least six weeks.
Cryotherapy
This is one of the effective methods of physiotherapeutic therapy, the essence of which is short-term local exposure of the affected area to extremely low temperatures (160-190°C) using liquid nitrogen.
As a result of this cooling, partial tissue denervation occurs and pain impulses are blocked. The course usually includes 10-15 daily procedures, and the effect occurs after the first sessions.
Intratissue electrical stimulation
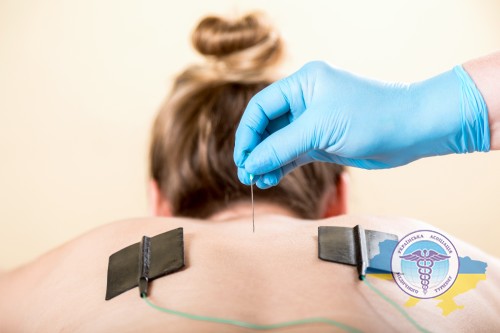
The method involves applying pulsed electric current directly to the affected area of the back. The procedure is absolutely painless and safe, as little power is used.
As a result, blood flow increases, congestion, swelling and inflammation are eliminated. Reparative processes in tissues are activated, and the pain syndrome significantly weakens after 1-2 procedures. The course of electrical stimulation is 10-15 sessions, which are carried out every other day.
Epidural catheterization according to Ratz
An equally effective procedure is epidural targeted pharmacotherapy according to Ratz. Under the control of X-ray navigation, a thin catheter is inserted into the epidural space of the spinal canal.
Through it, medications are administered over several days that have an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and absorbable effect directly into the lesion.
Surgical removal of intervertebral hernia
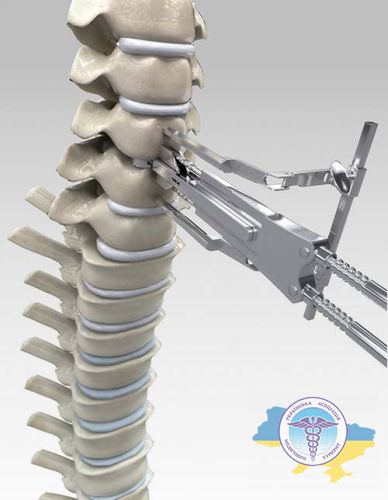
If minimally invasive therapy is ineffective, high-tech surgical methods are used. The most common methods for removing intervertebral hernia in Germany:
- Laminectomy (decompression). It involves the removal of part of the bone tissue (arch and spinous process) to relieve compression on the spinal cord and nerve endings. The procedure allows you to reduce or eliminate pain, as well as restore motor ability.
- Discectomy. It is the partial or complete removal of a damaged disc that is causing nerve compression. After surgery, fiber mobility is restored and pain is eliminated.
- Destruction of facet nerves. Involves the destruction of the neural processes that innervate the intervertebral joints. This leads to temporary pain relief, but does not eliminate the cause of the compression.
- Laser decompression. A minimally invasive procedure in which a laser light guide is inserted through a needle into the nucleus pulposus. The radiation evaporates part of the nucleus, which reduces the volume of the hernia and relieves pressure. Used in the initial stages to relieve symptoms.
- Vertebroplasty. A minimally invasive surgery in which polymethylmethacrylate-based bone cement is injected into the vertebra through a needle. The procedure strengthens weakened bone tissue and stabilizes vertebral body fractures. More often used for compression fractures due to osteoporosis.
- Microdiscectomy. An intervention in which the affected area is removed through an incision 1-2 cm long using an operating microscope. The procedure minimizes muscle and ligament damage compared to a traditional discectomy.
- Spiral nucleotomy. A procedure in which a special instrument with a spiral tip is inserted through a needle into the disc. By turning the instrument, the surgeon removes the fallen fragments and frees up space for the nerve roots.
- Hydroplasty. A procedure in which a special substance (hydrogel or balloon) is injected into the IVD under X-ray control. With the help of the drug, you can expand the fibrous ring, restore the height of the disc and stabilize the spinal segment.
- Prosthetics. An operation in which the removed damaged segment is replaced with an artificial implant. Thanks to the installation of the prosthesis, mobility is maintained and the development of spinal deformity is prevented.
- Stabilization. A surgical intervention aimed at fixing and immobilizing the vertebrae using special structures - systems of transpedicular screws, plates and rods.
Innovative techniques
Using modern technologies, medical specialists in Germany perform minimally traumatic operations, which ensures quick recovery and return to normal life.
Minimally invasive surgeries
Leading surgeons use endoscopes and operating microscopes to visualize the surgical field. This makes it possible to accurately recognize anatomical structures and perform manipulations through small incisions up to 1 cm. This approach preserves healthy tissue as much as possible, and patients can leave the clinic the very next day.
Robotic surgery
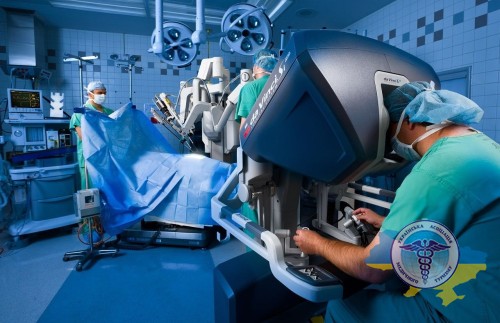
The use of robotics opens up the possibility of performing complex manipulations through punctures of 1-1.5 cm. The surgeon controls the robot, and the system filters hand tremors and converts movements into precise micro-movements of instruments.
Recent studies confirm that the use of robots increases the accuracy of operations and reduces the risk of complications. The success rate of removing intervertebral hernias using robot-assisted technology reaches 96%.
Epidural catheterization
Involves administering painkillers through a thin needle directly into the area between the dura mater and the wall of the spinal canal. The procedure helps deliver an anesthetic to the required area, relieve inflammation and swelling and reduce pressure on nerve endings, roots and spinal cord.
Laser decompression
An endoscopic technique in which a flexible light guide with a laser emitter is inserted into the spinal canal under visual control. Targeted laser action reduces the volume of protrusion, thereby relieving compression and unloading neural structures.
Chemonucliolysis
A minimally invasive method for the treatment of spinal hernia in German clinics, in which a drug based on the enzyme chymopapain is injected into the damaged intervertebral segment through a needle. It liquefies and dissolves scar tissue, as a result of which compression formation is reduced, and decay products are then removed.
Autohemotherapy
The method is based on the use of the patient's own blood, which is injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously. This stimulates the immune system and regenerative processes, triggers the restoration of damaged tissues and reduces inflammation. Used as an adjunct to other therapeutic tactics to avoid surgery.
Percutaneous intradiscal thermocoagulation
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, during which, using X-ray guidance, electrodes are inserted into the facet joints through which radiofrequency current is supplied.
It causes heating and coagulation of the neural processes innervating the joints. As a result, the transmission of pain impulses to the brain is interrupted. The effect lasts from 6 months to 2 years.
Nucleotomy
A tube with optics, instruments and a flushing system are inserted through the puncture. Under endoscopic control, fragments of the damaged disc that are compressing the nerve are removed. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to carry out the resection as carefully as possible under local anesthesia.
Transplantation of intervertebral disc cells
This is an advanced method of treating intervertebral disc herniation in Germany, thanks to which it is possible to slow down degenerative changes in the spinal column and start the process of its regeneration. The doctor collects healthy cells from the patient's disc tissue, which are then multiplied in the laboratory.
The culture obtained in this way is transplanted into the damaged intervertebral segment and stimulates the appearance of new healthy tissues in place of degenerative tissues.
B-Twin Method
This is a surgical technique for installing a special implant that increases the distance between the vertebrae. The use of this technology helps reduce pressure on the nerve and relieve pain. This operation allows you to avoid complete removal of the damaged vertebra.
Multifunctional electrodes (PASHA)
This is a modern neurostimulation system for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the spine, in particular with severe pain.
The principle of action is based on the delivery of weak electrical impulses to the structures of the spinal nerves in the epidural space. This leads to blockade of pain afferentation in the central nervous system and elimination of pain.
Percutaneous non-cleoplasty
The technology involves therapy using cold plasma energy. The puncture needle is inserted directly into the affected segment, thereby evaporating its contents. As a result, blood pressure is reduced and pain is relieved. Currently, the effectiveness of this method in German clinics reaches 90%.
Cost of treatment for spinal hernia in Germany
Prices for treatment of intervertebral hernia in Germany may depend on several key factors:
- Number of affected disks. The higher it is, the more difficult and lengthy the operation will be. Multiple lesions often require multiple implants or segment replacement.
- Prescribed medications. When choosing conservative therapy, the total cost is significantly influenced by the prices for prescribed drugs. In addition, the treatment regimen may include the simultaneous use of several medications over a long period of time.
- Method of therapy. Conservative treatment with medications and physical therapy, minimally invasive methods (epidural blockades) and surgery are available to choose from. Surgery is usually the most expensive, especially if it is a complex procedure involving implants.
- Localization. The cost is also affected by the location of the pathology (cervical, thoracic or lumbar). The higher the localization, the more difficult and expensive the surgery will be.
- Direction of protrusion. If it occurs towards the spinal cord, the operation will be technically more difficult and dangerous than in the lateral direction.
- Type of medical facility. Therapy in public clinics in Germany is cheaper, but there can be long queues for planned operations. In private medical centers, service and comfort are higher, and therefore the price of therapy will also be more expensive.
The table shows approximate prices:
| Procedure | Cost, € |
|---|---|
| Consultation with a neurosurgeon | from 1200 |
| Orthopedist consultation | from 200 |
| Diagnostic MRI | from 390 |
| Epidural block | from 590 |
| Decompressive laminectomy | from 9300 |
| Microdiscectomy | from 10900 |
| Installation of interspinous implants | from 13600 |
| Postoperative rehabilitation | from 2300 |
| Physiotherapy (10 sessions) | from 550 |



