Treatment of brain cancer in clinics of Germany
Brain cancer is a fairly rare but extremely dangerous disease. Its main difficulty lies in the fact that the malignant tumor is located in proximity to vital parts of the body - large vessels, nerve centers and the hypothalamus. Therefore, its removal requires special care and precision of the surgeon.
Patients from all over the world come to Germany for treatment of brain cancer, since German clinics are famous for using advanced techniques and innovative drugs. Thanks to the high professionalism of European neurosurgeons, cancer patients can count on successful brain treatment in Germany and subsequent recovery in the vast majority of cases.

Want to know how much the treatment costs?
Answer a few questions and get preliminary information about the cost of diagnosis and treatment!
Advantages of brain cancer treatment in Germany
Today, German medical institutions occupy leading positions in the world in terms of diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the central nervous system. Among the decisive advantages of brain cancer treatment in Germany:
- High level of medicine. It was achieved thanks to significant government investments in healthcare - the country ranks 2nd in the world in this indicator. Budget funds are used to update equipment, research and improve the quality of services for cancer patients.
- Strict quality control. The admission of foreign cancer patients is strictly controlled by the state. To obtain permission, the medical center must meet the requirements for the qualifications of personnel, the level of service and the effectiveness of treatment programs.
- Efficiency. German neurosurgeons specialize in high-tech endoscopic operations to remove tumors. They perform minimally invasive resections through 1-2 small holes in the skull or through the nasal passages. This allows you to preserve healthy tissue as much as possible and reduce the recovery period to 1 week.
- Innovative approach. Medical institutions are actively introducing the latest developments in the field of oncology, neurology and other areas. Clinical studies are conducted in research centers and universities, and the most effective methods are included in therapeutic programs.
- Modern equipment for radiotherapy. Medical centers use advanced installations with 3D planning. This makes it possible to increase the accuracy of tumor irradiation to 0.5 mm, which is critical for preserving healthy tissue.
- Use of 3D visualization. To minimize the risks of complications, surgeons use a special MRI-based program. This allows you to examine in detail the anatomy of the organ being examined and accurately plan surgical intervention. The doctor sees the location of the instruments and knows where to make the incisions in order to preserve the functions of the nervous system as much as possible.
- Rehabilitation. After surgery, it is important to begin recovery as early as possible in order to stimulate compensatory mechanisms. The centers' specialists - neurologists, physiotherapists, speech therapists and occupational therapists - develop personalized programs taking into account the location and characteristics of the affected area.
What types of brain tumors are treated in Germany?
German medical centers take on all types of oncology of the central nervous system. Patients with the following pathologies can count on treatment for brain cancer in Germany:
- Gliomas. The most common type of disease that develops from neuroglia, the supporting tissue of the nervous system. There are benign and malignant. The latter include glioblastomas - the most aggressive type of gliomas, which are characterized by intense growth, necrosis and cerebral edema.
- Medulloblastoma. Fetal cancer pathology, which mainly occurs in children 5–10 years old. It is localized in the cerebellum and tends to spread along the central spinal canal. A positive result is achieved using surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
- Meningioma. It comes from the membranes of the organ and is asymptomatic in the first stages. Most often it occurs in a benign form, less often in a malignant form. Often treated surgically or with radiation.
- Pituitary adenoma. A benign formation of the anterior pituitary gland, which causes hormonal disorders associated with overproduction of hormones. Treated with surgical or endoscopic removal.
- Neurinoma. It develops from the sheaths of peripheral nerves and fibers. A distinction is made between neuroma of the auditory nerve and cranial nerves (trigeminal, facial, etc.). Treated surgically or using stereotactic radiosurgery.
How is a brain tumor diagnosed in German clinics?
To effectively diagnose brain tumors, European doctors use the following methods.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the main examination methods to obtain a detailed image of the anatomical structure and location of the formation in three dimensions.
Its main advantages are the absence of radiation exposure, the ability to scan in various planes and high contrast. Using MRI, you can detect cancer in the early stages, determine its size, boundaries and relationship with functionally significant areas.
MR spectroscopy
This type of research provides information about the biochemical composition of tissues and the metabolic process. Cancer cells have a biochemical composition different from normal ones, which helps determine the type of pathology and evaluate the effect of the chosen therapeutic strategy. MR spectroscopy is a non-invasive method that is performed in addition to standard MRI.
Computed tomography
CT creates detailed images using X-rays, which helps to assess the condition of not only internal organs, but also the bones of the skull.
Computed tomography takes about 15–50 minutes and is often prescribed if there are contraindications to MRI. The patient is placed in a machine that takes several pictures from different angles. The images are then processed by computer to produce accurate 3D models.
PET-CT
The examination combines positron emission tomography and computed tomography and helps detect relapse. Before scanning, the patient is injected intravenously with a radioactive drug that concentrates in cancer cells.
The patient is then placed in a two-part apparatus. One part records accumulations of the drug, and the second takes X-ray images of the body. Next, the computer combines images in which you can see the exact location of the tumor. PET-CT is also often used to search for metastases.
Biopsy
This study determines the stage of development of the pathology, which allows you to select effective therapy. A biopsy is performed separately or during surgery by removing a piece of biological material through an opening in the skull.
Computer navigation is used to obtain the sample. It calculates the trajectory of the needle, thereby making the procedure safe and less traumatic. The resulting material is examined under a microscope, and the results are usually ready within 5–10 days.
Positron emission tomography
PET is a non-invasive imaging technique that analyzes metabolic activity. It is based on the introduction of radioactive molecules into the body, which are concentrated in metabolically active zones.
PET is used to detect pathologies, assess their malignancy and monitor the response to a therapeutic course. This study helps to identify oncology at the earliest stages, before the appearance of anatomical changes. PET is also useful for biopsy and surgical planning.
Myelography
This is an X-ray examination of the spinal canal with the introduction of a contrast agent, which is used to evaluate cancer of the spine and identify possible metastases.
Myelography is performed on an outpatient basis and takes about 5–10 minutes. By contrasting the structures, a clear image of the spine and possible pathological changes is obtained, which helps to detect compression and foci of destruction of the vertebrae.
Spinal tap
This minimally invasive procedure involves removing a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal. The resulting sample is sent for cytological and biochemical examination. The presence of pathological changes in the sample or elevated levels of specific proteins may indicate tumor or metastatic lesions.
Electroencephalography
The examination records electrical activity and helps determine the location of the cancer focus, which can often be the cause of epileptic seizures. By comparing the EEG in normal conditions and during an attack, doctors determine the area responsible for epileptiform activity.
Long-term EEG video monitoring recording over several days is the most informative. It records the electrical activity of the organ in different states and helps to accurately localize the epileptogenic focus.
Methods of treating brain tumors in German clinics

The choice of therapeutic tactics depends on the location, stage of the process, general condition of the patient and the presence of metastases. Therefore, advanced diagnostic methods and treatment programs for oncological diseases of the central nervous system are widely used in medical institutions.
Surgery
Surgery is the main therapeutic method. The choice of a specific type of surgery depends on the characteristics of the formation - histological type, location, size, vascularization and relationship to functionally significant areas.
Endoscopic surgery
This is a minimally invasive technique in which access is made through holes in the skull with a diameter of 8-15 mm. An endoscope, an optical device that provides illumination and visualization of the surgical field, as well as microsurgical instruments, is inserted through these holes. Thanks to endoscopic access, the tumor is removed under visual control in order not to damage functionally significant structures.
Transnasal surgery
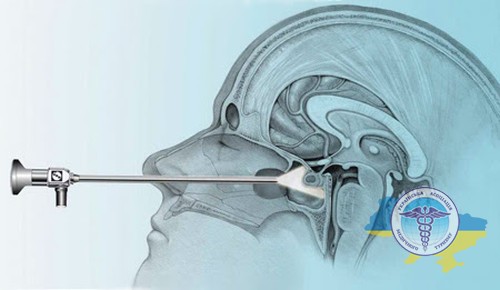
For small lesions in accessible areas, low-traumatic endoscopic and transnasal operations are used. They allow the affected areas to be removed through the natural nasal passages or an opening in the skull. Such interventions ensure rapid recovery and a minimum of complications.
Craniotomy
For extensive or difficult-to-reach lesions, an open craniotomy is performed - dissection of the skull bones to access the affected area. Sometimes such effects are carried out under local anesthesia. In this case, the patient is conscious during the operation, which allows the surgeon to control motor and speech functions and prevent their damage.
Conservative therapy
In addition to surgery, a set of additional procedures is widely used for malignant diseases of the central nervous system.
Radiotherapy
This is the second most popular therapeutic method, in which the formation is irradiated to reduce its size or suppress growth. Radiotherapy is the main method (for inoperable or hard-to-reach cases) and additional (after incomplete removal).
To treat brain cancer, clinics in Germany use high-precision radiosurgical equipment - gamma knife, cyber knife and linear accelerators. These technologies form beams of ionizing radiation that converge at one point and follow the contours of the formation.
Due to the high precision of exposure, healthy tissues receive minimal radiation exposure, which significantly reduces the risk of complications compared to traditional irradiation.
Chemotherapy
It is not used in all cases, since not all cancers are sensitive to chemotherapy. Depending on the specific indications, it is prescribed intravenously or in tablet form.
The main goal of chemotherapy is to destroy the remaining pathological cells to reduce the risk of relapse. For inoperable tumors, chemotherapy is combined with radiotherapy to slow the growth and spread of cancer, including metastases.
Immunotherapy
This is an innovative approach that involves stimulating the patient’s own immunity to recognize and destroy cancerous foci. A well-known example of the successful use of immunotherapy is the cure for metastases in the living former US President Jimmy Carter, who was 91 years old at the time the disease was discovered.
However, immunotherapy is not yet a universal method and does not bring results for all cancer patients. Scientists continue to work on creating more effective drugs and treatment regimens that will make it possible to fight cancer even at terminal stages.
Targeted therapy
According to research, targeted drugs selectively affect cancer tissue and do not damage healthy areas, which reduces side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
This technique is prescribed for glioblastomas and giant cell astrocytomas. The specific regimen and duration of therapy is determined by the attending oncologist.
Innovative techniques
In German medical institutions, cancer patients have the opportunity to undergo a therapeutic course using advanced technologies that have already been introduced into clinical practice, or to take part in research programs.
Minimally invasive surgeries
Minimally invasive interventions significantly reduce the trauma of surgery and speed up rehabilitation. In particular, approaches through the nasal passages, oropharynx or even the middle ear are used. In addition, some ventricular lesions can be excised through small holes at the hairline using endoscopic techniques.
Ablation
Laser ablation makes it possible to effectively combat various forms of oncology, avoiding open traumatic resections. Through a hole in the skull (about 3 mm in diameter), a thin laser fiber is applied to the pathological area.
Directed radiation locally destroys pathological lesions without damaging surrounding healthy areas. The entire procedure is monitored using a magnetic resonance imaging machine in real time.
Brachytherapy
This is local radiotherapy, in which radioactive sources (most often iodine-125 or iridium-192) are implanted into the tumor or into the cavity after its removal. This allows you to deliver a high dose of γ-radiation directly to the problem area and minimize damage to surrounding tissue.
Used both separately and in combination with radiotherapy. Brachytherapy shows good effectiveness in primary and metastatic lesions.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
This is high-precision radiation exposure to the affected area from many narrow beams at different angles. In 1–5 sessions, a high dose can be delivered to primary and metastatic lesions with minimal irradiation of healthy tissue.
Radiosurgery uses 3D imaging technology and robotic arms for precise positioning. Effective for small and medium-sized tumors and is often used in combination with resection.
Cryosurgery
This is a method of cancer destruction through local extreme cooling with special cryoprobes to temperatures of -160-190°C. Cells and microvessels are destroyed, and immune mechanisms are launched, stimulating the body's natural response against pathology.
This is a low-traumatic impact that can be used for hard-to-reach or functionally significant areas. Cryosurgery is effective for small pathologies and residual volumes after resection.
How does rehabilitation occur after treatment for a brain tumor?
The speed of recovery after treatment of a brain tumor in Germany largely depends on the location and size of the tumor, as well as the degree of damage to functional areas. According to experts, some patients with small tumors do not require rehabilitation - they return to their normal lifestyle within 2–3 weeks.
However, large cancerous lesions often lead to permanent neurological impairment. In such cases, postoperative recovery is of fundamental importance and consists of the following points:
- Therapeutic exercise. It includes classes with a physical therapy instructor, the use of special machines and exercises to improve movement control and endurance training.
- Occupational therapy. Necessary for practicing self-service skills and performing familiar household tasks - cooking, cleaning, driving a car, using household appliances, etc.
- Classes with a speech therapist. Must be prescribed for speech and communication disorders - aphasia of various types, dysarthria and stuttering. Special training is used to restore the functions of the vocal cords, articulation, expand vocabulary and speech perception.
- Classes with a neuropsychologist. They are carried out in cases of severe cognitive impairment - disorders of memory and attention, as well as the ability to learn and make decisions. Brain functions are tested, and individual exercises are selected for their training using specialized computer technologies.
- Psychotherapeutic assistance. Included in the course to overcome emotional disorders and personality changes - anxiety, depression or irritability. The program takes place both individually and in group form.
Cost of treatment for brain cancer in German clinics
Therapy is prescribed in accordance with an individual plan drawn up for each patient, taking into account the specific clinical situation. Below are the key factors that influence the final price of brain cancer treatment in Germany:
- Stage of the disease. The earlier cancer is detected, the easier and cheaper it is to cure. Advanced forms of oncology require longer and more resource-intensive therapy.
- Type and extent of surgery. Open and laparoscopic procedures vary significantly in cost. The difference also lies in the volume of lesions removed - organ-preserving or radical operations are performed.
- Additional methods. Here it is necessary to take into account the number and duration of chemotherapy courses, the type of chemotherapy drugs used and the need for targeted and immunotherapy. The type and duration of radiation exposure during radiotherapy also play a significant role.
- Hospitalization. Its cost increases with complications, repeated courses, stays in intensive care units.
- Clinic. The price is significantly influenced by the type of medical institution (public or private), its degree of equipment with modern diagnostic equipment and the qualifications of oncologists. In private medical centers, the cost of services is usually higher.
- Rehabilitation. Upon completion of therapy, medical rehabilitation is often required using physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage, psychotherapy, as well as recovery from possible surgical complications or a sanatorium-resort program.
Estimated cost of treatment for brain tumors:
| Procedure | Cost, € |
|---|---|
| Contrast-enhanced MRI | 865 |
| Consultation with a neurosurgeon | 1077 |
| Radiation therapy, full course | 8330 |
| Radiosurgery (gamma knife), 1 session | 8050 |
| Craniotomy | 18750 |
| Open access tumor removal | 9340 |
| Glioma removal | 24500 |
| Laser ablation | from 5000 |



