Treatment of liver cancer in clinics of Germany
Liver cancer ranks 5th among all cancer diseases in terms of incidence. About 500,000 new cases are diagnosed worldwide every year. In most cases, this disease affects men over 45 years of age.
More recently, the diagnosis of liver cancer was considered practically a death sentence, however, today the situation has undergone dramatic changes. Successful treatment of this disease is carried out in clinics in Germany.
Thanks to the use of innovative diagnostic methods, medications and high-tech surgical techniques, treatment of liver cancer in Germany leads to recovery even in the 4th, most advanced stage of the disease.
Patients in German cancer centers are treated by a multidisciplinary team of specialized specialists who use innovative methods of targeting the tumor without affecting healthy tissue. Also, German doctors constantly conduct research in search of alternative treatment methods and successfully implement them in practice.

Do you want to know how much the treatment costs?
Answer a few questions and get a preview of the cost of diagnosis and treatment!
Advantages of liver cancer treatment in Germany
German medicine is considered one of the most advanced in the European Union thanks to significant government investments in the development of healthcare. This allows you to regularly update clinic equipment, conduct research and introduce new techniques, and improve the quality of medical services.
The advantages of liver oncology treatment in Germany include:
- High level of provision of medical services. All clinics accepting foreign patients undergo strict certification by the German Ministry of Health. This guarantees a high level of qualifications of doctors, modern equipment of clinics, and quality of treatment in accordance with international standards.
- Innovative technologies. The country's oncology centers use both their own developments and the achievements of world medical science. For example, in the treatment of liver cancer, high-precision equipment for radiosurgery, the latest methods of tumor embolization, and targeted therapy are used. University clinics are conducting research in the field of immunotherapy and cancer gene therapy.
- Personalized approach. For all patients, an individual treatment program is developed taking into account the characteristics of the disease at an interdisciplinary consultation. It includes oncologists, surgeons, radiologists and other specialists. Such a comprehensive assessment allows you to select the most effective tactics in each individual case.
- Treatment protocols. Based on the recommendations of leading European specialized communities - ESMO and DKG. This ensures that treatment is carried out in accordance with the most modern international standards. Regularly updated clinical guidelines allow you to apply the latest scientific advances in practice.
- Use of gentle, minimally invasive methods. Whenever possible, German oncologists try to use high-tech methods of surgical treatment of liver oncology - radiofrequency thermal ablation of the tumor, CyberKnife radiosurgery, etc. This allows you to remove the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding tissue and speed up postoperative recovery.
Diagnostics of liver oncology in Germany
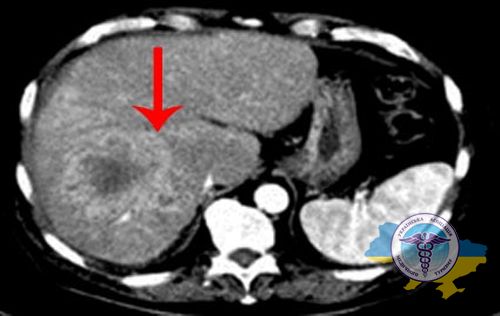
To diagnose liver cancer in Germany, a complex of modern high-precision methods is used to accurately determine the location, size and characteristics of the tumor. We use advanced diagnostic equipment, regularly updated in accordance with the latest advances in medical technology.
The initial examination includes taking an anamnesis, examining the patient, and laboratory tests of blood, urine and other biological fluids. Tumor markers are determined, for example, alpha-fetoprotein, the level of which may indicate the presence of a tumor process in the liver.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. A non-invasive method, which is performed primarily if liver pathology is suspected. Allows you to obtain primary information about its condition, structure, size. Identifies space-occupying formations, foci and lesions. Ultrasound is highly accessible, safe, and can be reused for condition monitoring.
- CT and MRI with contrast. Provides enhanced visualization of the abdominal organs. Computed tomography is performed using X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging is based on radio waves and a magnetic field. These methods make it possible to obtain a multilayer image and accurately determine the location, size, characteristics of the tumor, and the degree of tissue damage. Contrast improves visualization of vessels and pathological areas.
- PET-CT. A radioisotope method based on the introduction of a weakly radioactive tracer into the body. It accumulates in pathological foci, which makes it possible to detect even small metastases throughout the body. PET-CT is highly sensitive and can detect tumors up to 1 mm in size. This is important for determining the stage of the disease and choosing treatment tactics.
- Laparoscopy. A minimally invasive endoscopic method in which a special tube with a camera and a light is inserted through small punctures. This allows you to examine the abdominal organs in detail, identify pathological changes at an early stage, and clarify the extent of the tumor process. During laparoscopy, targeted tissue sampling for histological examination is possible.
- Fusion biopsy. An invasive procedure in which cells are collected directly from the lesion using a special needle. It is carried out under visual ultrasound control for more precise targeting of the required area. The obtained samples are examined under a microscope, which makes it possible to determine the nature and degree of malignancy of the tumor.
- Angiography. A method for studying the vessels of the liver and the arteries supplying it. It is carried out by introducing a contrast agent and fluoroscopy. Allows you to evaluate the vascularization of the tumor, which is important for planning surgical treatment.
Data obtained during the examination are analyzed by medical specialists. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, a protocol for further treatment using innovative technologies is developed.
Methods of treatment of liver cancer in German clinics
To treat liver cancer, clinics in Germany use the entire arsenal of modern technologies, both surgical and therapeutic. This allows you to select personalized tactics for each specific patient, taking into account the stage and characteristics of the tumor.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is one of the main methods of treating liver cancer, allowing radical elimination of the tumor.
In German clinics, various types of liver resections are performed depending on the location and size of the tumor:
- Left lobectomy - removal of the left lobe of the liver.
- Left-side hemihepatectomy - removal of the left segments (II, III and IV) of the liver.
- Right hemihepatectomy - removal of the right segments (V, VI, VII and VIII) of the liver.
If the tumor is small, atypical resection can be performed - removal of only the affected area of the liver parenchyma.
German surgeons are highly qualified in liver surgery, which allows them to achieve good results even with complex tumors. They use both open and minimally invasive laparoscopic methods, which reduce the invasiveness of the operation. In case of extensive damage, liver transplantation is performed.
Conservative techniques
Conservative techniques are aimed at destroying cancer cells, controlling tumor growth and preventing metastasis. This includes methods that affect the patient's entire body through the bloodstream, without resorting to surgery. They are used both as independent therapy in the early stages of the disease, and in combination with other methods.
Radiation therapy
It involves exposing the tumor to ionizing radiation in order to damage the DNA of cancer cells and disrupt their ability to divide and grow. In Germany, modern types of radiation are used - conformal radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery.
They allow you to target the tumor as precisely as possible, sparing healthy tissue. Radiation therapy can be used as a stand-alone method or in combination with other types of antitumor treatment.
Chemotherapy
A method based on the use of special drugs - cytostatics, which disrupt the processes of division and growth of cancer cells. German oncology clinics use the latest chemotherapy regimens, taking into account the histological type of tumor and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Chemotherapy can be given intravenously, intra-arterially, or orally. It is effective at all stages of the disease, including metastases.
Targeted therapy
Targeted effects on molecular targets in cancer cells using special drugs. This allows you to disrupt the mechanisms responsible for the growth and spread of the tumor.
Targeted drugs that block angiogenesis, growth factors and signaling pathways in tumor cells can be used to treat liver cancer.
Minimally invasive methods of treating oncology
In addition to radical treatment methods, gentle, minimally invasive technologies are widely used in German clinics to effectively combat tumors with minimal stress on the body. They are especially relevant for patients with severe concomitant diseases.
Embolization
A procedure in which the lumen of the vessels feeding the tumor is closed using microspheres. Embolization is effective for both primary and metastatic liver tumors.
The most common types of such procedures are:
- Chemoembolization. Spheres are used that release cytotoxic agents over a period of weeks. This creates a high concentration of the drug directly at the site, suppressing tumor growth. As a result of exposure, the size of the tumor can decrease several times. The method is effective for both primary and metastatic tumors.
- Radioembolization. A more rare procedure, during which spheres saturated with radioactive yttrium-90 destroy tumor cells from the inside. The method has been used since 2016 and is indicated for inoperable liver cancer.
Ablation
Destruction of the tumor by physical methods - radio frequency, microwaves, ultrasound. Allows you to locally influence the tumor while preserving the surrounding tissue.
The most common is radiofrequency ablation - the tumor is heated to a temperature above 60°C by electromagnetic waves through a needle-electrode. Another promising direction is microwave ablation, which uses electromagnetic radiation in the microwave range. Allows you to destroy tumors up to 8 cm in just a few minutes.
Radiosurgery (Cyber Knife)
A method of high-precision radiation therapy, in which dozens of radiation beams are exposed to the tumor from different angles during the session. This allows the dose to be focused as much as possible on the lesion without affecting healthy tissue.
Cyberknife is effective for tumors up to 5 cm located close to blood vessels. It provides the highest precision and minimal trauma, which allows you to make treatment as personalized and gentle as possible for a particular patient.
Innovative methods
German oncologists are actively developing and implementing innovative methods of treating hepatocellular cancer, which can significantly improve the results of treatment of this serious disease. Among the most promising areas:
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A minimally invasive procedure in which chemotherapy drugs are injected into the hepatic artery in combination with embolic agents. This makes it possible to deliver a high concentration of antitumor drugs directly to the lesion and enhance their effect due to ischemia. Median survival after TACE is 20 months.
- Cryosurgery. Local destruction of the tumor using extremely low temperatures. Used for small tumors (up to 3 cm). Allows to achieve 3-year survival in 15-20% of patients.
- Ethanolization. Injection of concentrated ethanol directly into the tumor under ultrasound guidance. Used to treat inoperable patients. Comparable in effectiveness to resection.
- Intratissue radiation therapy (brachytherapy). Implantation of radioactive sources directly into the tumor. Allows you to deliver a high dose of radiation to the affected tissues, minimizing the radiation dose to surrounding healthy structures.
- Electroporation (IRE). Destruction of tumor cells by short-term high voltage pulses. Used in combination with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy. Helps block the mechanisms by which tumor cells evade immune surveillance. This allows you to activate antitumor immunity in the patient’s body.
- CAR-T therapy. Genetic modification of patient T lymphocytes to recognize tumor cells. Used for relapsed and refractory hepatocellular cancer. Allows to achieve complete remissions in a number of patients.
Prices for liver cancer treatment in Germany
Although the cost of treatment for liver cancer in Germany is slightly higher than in Israel or Turkey, therapy in this country is highly effective due to the use of innovative techniques and advanced equipment.
The final price of treatment is calculated individually for each patient, taking into account the necessary manipulations and depends on the stage and extent of the tumor process, the volume of required surgical intervention, the methods used, length of hospitalization and rehabilitation measures.
At the same time, average prices are in the following range:
| Procedure | Cost, € |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis | 2000-5000 |
| Liver biopsy | 3000-10000 |
| Liver resection | 8000-15000 |
| Liver transplantation | от 80000 |
| Chemoembolization | 5000-9000 |
| Local ablation | 5000-15000 |
| Systemic chemotherapy, 1 course | 3000-6000 |
| Radiation therapy, 1 course | 2000-5000 |
For a preliminary estimate of the cost of treatment in a specific German clinic, provide medical documents about the diagnosis and condition of the patient to our consultant. This will allow doctors to develop an optimal therapy program and calculate an approximate estimate for all expected costs.



